Handle PostgreSQL® node replacements when using Debezium for change data capture
When you run a Debezium source connector for PostgreSQL® with an Aiven for PostgreSQL® service, some database operations can interrupt change data capture (CDC).
For example, if the PostgreSQL service undergoes an operation that replaces nodes (such as maintenance, a plan change, a cloud region change, or a node replacement), the Debezium connector can lose its connection to the database.
In many cases, Debezium resumes CDC after the connector tasks restart. In some cases, the PostgreSQL replication slot used by Debezium starts lagging. This can cause WAL files to accumulate and increase disk usage.
Use the GitHub repository to set up and test a Debezium node replacement scenario. For guidance, see the Aiven Debezium test repository.
Common Debezium errors during PostgreSQL node replacement
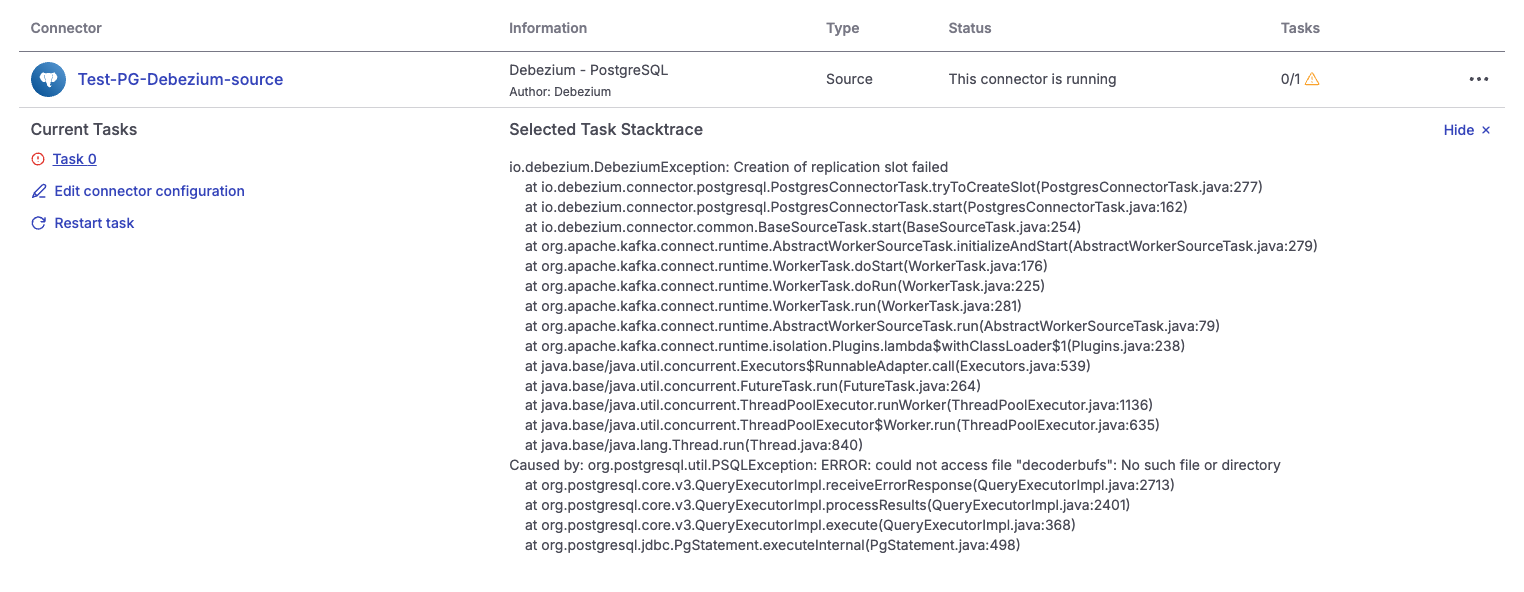
If the Debezium connector cannot recover during or after a PostgreSQL node replacement, the following errors commonly appear in the logs:
# ERROR 1
org.apache.kafka.connect.errors.ConnectException: Could not create PostgreSQL connection
# ERROR 2
io.debezium.DebeziumException: Could not execute heartbeat action (Error: 57P01)
# ERROR 3
org.PostgreSQL.util.PSQLException: ERROR: replication slot "SLOT_NAME" is active for PID xxxx
These errors are not recoverable automatically. Restart the connector tasks to resume CDC. You can restart connector tasks in one of the following ways:
- Aiven Console: Open the service where the connector is running and go to Connectors.
- Kafka Connect REST API: Send the request to the Kafka Connect REST API endpoint.
To find the Kafka Connect service URI, open the Aiven Console and go to the Aiven for Apache Kafka Connect service used by the connector. On the Overview page, under Connection information, copy the value in Service URI.
To automatically restart failed tasks, set _aiven.restart.on.failure=true in the
connector configuration.
Aiven checks task status every 15 minutes by default. You can change the interval if needed. For details, see Enable automatic restart.
Handle growing replication lag after Debezium connector restart
As described in the Debezium documentation, replication lag can increase after the connector tasks restart for two common reasons:
-
High write volume in the database: Many updates occur in the database, but only a small portion affects the tables and schemas Debezium monitors. In this case, Debezium might not advance the replication slot fast enough to prevent WAL files from accumulating.
To address this issue, enable periodic heartbeat events by setting
heartbeat.interval.ms. -
Multiple databases on the same PostgreSQL instance:
One database generates high write traffic, while Debezium captures changes from a low-traffic database. Replication slots operate per database, so Debezium cannot advance
confirmed_flush_lsnunless it receives events for the monitored database.Because WAL is shared across databases, WAL files can accumulate until Debezium receives an event from the monitored database.
In Aiven testing, this behavior occurred in the following scenarios:
-
The monitored tables had no changes and heartbeat events were not enabled.
-
The monitored tables had no changes, heartbeat events were enabled (
heartbeat.interval.msandheartbeat.action.query), but the connector did not emit heartbeat events.noteThis heartbeat issue is tracked in Debezium bug DBZ-3746.
Clear the replication lag
To clear replication lag, generate activity on monitored tables so Debezium can advance the replication slot:
- Resume database traffic (if you paused writes).
- Make a change to any monitored table.
After Debezium processes the event, it updates the confirmed LSN and PostgreSQL can reclaim WAL space.
Ensure Debezium survives a PostgreSQL node replacement
To prevent missing CDC events during node replacement and ensure Debezium recovers correctly, use one of the following approaches.
Recover safely from Debezium failures
This approach prevents missing events by stopping writes to the source database until Debezium recreates the replication slot on the new primary.
-
Stop write traffic to the database immediately. After node replacement, replication slots are not recreated automatically on the newly promoted primary. When Debezium recovers, it recreates the replication slot.
If writes occur before the slot is recreated, Debezium cannot capture those changes.
If you must recover missing data, temporarily set
snapshot.mode=alwaysand restart the connector tasks. This republishes snapshot data to the Kafka topics.After the snapshot completes, restore the configuration to the default to avoid generating a snapshot on every restart.
-
Restart the failed connector tasks.
-
Verify that the replication slot exists and is active. Query
pg_replication_slotsand confirm the slot is present and active. -
Resume write operations.
Automate replication slot recreation and verification
This approach requires an automated process that recreates the replication slot on the new primary after node replacement.
Debezium recommends recreating the replication slot before allowing applications to write to the new primary:
There must be a process that re-creates the Debezium replication slot before allowing applications to write to the new primary. This is crucial. Without this process, your application can miss change events.
Debezium can recreate the replication slot after it recovers, but this can take time. An automated process that recreates the slot immediately after node replacement reduces downtime and lowers the risk of missed change events.
When Debezium restarts, it reads all changes written after the replication slot is created.
The example in the Aiven test repository blocks inserts unless the Debezium replication slot is active.
In most cases, it is sufficient to verify that the replication slot exists, even if it is inactive. Once the connector resumes CDC, it reads all changes written since the slot was created.
Debezium also recommends verifying that it has read all changes from the replication slot before the old primary failed.
To ensure downstream consumers receive all events, implement a verification method that confirms changes to monitored tables were recorded.
The Aiven test repository includes an example implementation.
Handle PostgreSQL major version upgrades
A PostgreSQL major version upgrade replaces database nodes. This can interrupt Debezium change data capture (CDC) in the same way as a PostgreSQL node replacement.
During the upgrade, Debezium tasks can fail and the replication slot might not be available immediately on the new primary. If applications write to monitored tables before the slot is recreated, downstream consumers can miss change events, leading to potential data loss.
For guidance, see Steps to protect against data loss when using Debezium and upgrading the PostgreSQL source.
Related pages